前言
前两篇主要介绍了C++对象在一级继承体系下的对象模型,接下来将考虑二级继承体系下常用的菱形继承对象模型的影响和变化,主要包括普通菱形继承和虚拟菱形继承
菱形继承
普通菱形继承类
公共基类简单实现代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class B
{
public:
B(int var = 10): _b(var){};
~B() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "B Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunB(void)
{
std::cout << "B RunB()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _b;
};
|
普通菱形继承类简单实现代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| class D1 : public B
{
public:
D1(int var = 20): B(var),_d1(var) {};
~D1() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "D1 Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunD1(void)
{
std::cout << "D1 RunD1()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _d1;
};
class D2 : public B
{
public:
D2(int var = 20) : B(var), _d2(var) {};
~D2() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "D2 Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunD2(void)
{
std::cout << "D2 RunD2()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _d2;
};
class Rhombus : public D1, public D2
{
public:
Rhombus(int var = 30) : D1(var), D2(var), _rhombus(var) {};
~Rhombus() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "Rhombus Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunRhombus(void)
{
std::cout << "Rhombus RunRhombus()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _rhombus;
};
|
Gcc命令的内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| Vtable for Rhombus
Rhombus::_ZTV7Rhombus: 11 entries
0 (int
(...))(& _ZTI7Rhombus)
16 (int
(...))B::RunB
32 (int
(...))Rhombus::RunRhombus
48 (int
(...))(& _ZTI7Rhombus)
64 (int
(...))B::RunB
80 (int
|
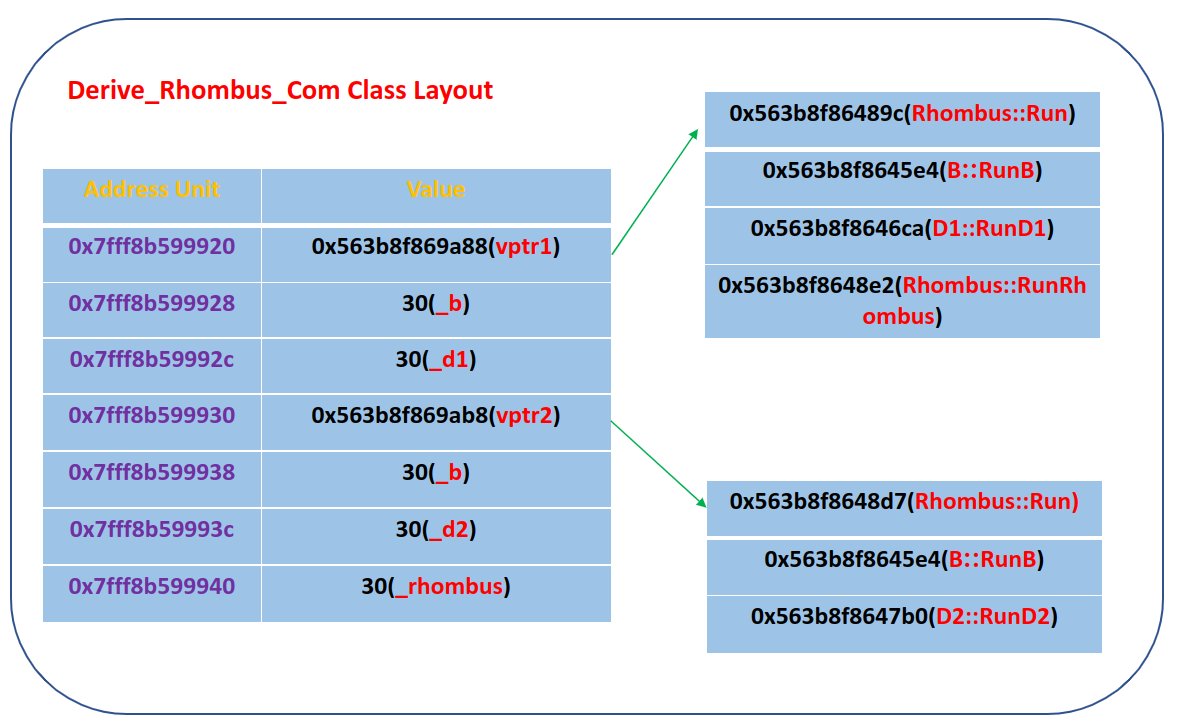
可以看到普通菱形继承类的内存空间特点是基类Di的内存布局(按照继承的顺序依次布局基类)+子类的成员变量,基类Di的内存布局包括公共基类B的内存布局和基类Di的成员变量。子类的虚函数在继承而来的第一个继承的Di基类的虚函数表基础上进行替换(override),新增子类(新的虚函数),保持操作(没有override)。可以看到普通菱形继承内存中存在多份公共基类B的结构,这样存在二义性的问题,如对于Rhombus类调用Run方法,由于两个子类D1,D2都重写了,且都继承来了,不知道调用哪个子类的方法
内存布局的代码验证
1.测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| void RhombusCommonDeriveTest(void)
{
Rhombus d;
std::cout << "---------begin rhombus common derive object inner memory layout test-------" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object size is: " << sizeof(d) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object addr is: " << &d << std::endl;
std::cout << " typeid(d) is: " << typeid(d).name() << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d1 obj begin -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr addr is: " << (long*)*(long*)&d << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[0] func ptr is: " << (long*)*(long*)(*(long*)&d) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[0] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRun = (pFunc)(*(long*)(*(long*)&d));
(*pRun)();
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[1] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[1] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunB = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 1));
(*pRunB)();
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[2] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[2] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunD1 = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 2));
(*pRunD1)();
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[3] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 3) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[3] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunRhombus = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 3));
(*pRunRhombus)();
std::cout << " object _b addr is: " << (long*)&d + 1 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _b value is: " << (int)*((long*)&d + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d1 addr is: " << (long*)((int*)((long*)&d + 1) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d1 value is: " << *((int*)((long*)&d + 1) + 1)<< std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d1 obj end -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d2 obj begin -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr addr is: " << (long*)*((long*)&d + 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[0] func ptr is: " << (long*)*(long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[0] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRun2 = (pFunc)(*(long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)));
(*pRun2)();
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[1] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[1] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunB2 = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 1));
(*pRunB2)();
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[2] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[2] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunD2 = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 2));
(*pRunD2)();
std::cout << " object _b addr is: " << (long*)&d + 3 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _b value is: " << (int)*((long*)&d + 3) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d2 addr is: " << (long*)((int*)((long*)&d + 3) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d2 value is: " << *((int*)((long*)&d + 3) + 1)<< std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d2 obj end -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _rhombus addr is: " << (long*)&d + 4 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _rhombus value is: " << (int)*((long*)&d + 4) << std::endl;
std::cout << "---------end rhombus common derive object inner memory layout test-------" << std::endl;
}
|
2.运行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| ---------begin rhombus common derive object inner memory layout test-------
object size is: 40
object addr is: 0x7fff8b599920
typeid(d) is: 7Rhombus
------ d1 obj begin -----
object d1 vfptr addr is: 0x563b8f869a88
object d1 vfptr[0] func ptr is: 0x563b8f86489c
object d1 vfptr[0] func invoke res: Rhombus Run()
object d1 vfptr[1] func ptr is: 0x563b8f8645e4
object d1 vfptr[1] func invoke res: B RunB()
object d1 vfptr[2] func ptr is: 0x563b8f8646ca
object d1 vfptr[2] func invoke res: D1 RunD1()
object d1 vfptr[3] func ptr is: 0x563b8f8648e2
object d1 vfptr[3] func invoke res: Rhombus RunRhombus()
object _b addr is: 0x7fff8b599928
object _b value is: 30
object _d1 addr is: 0x7fff8b59992c
object _d1 value is: 30
------ d1 obj end -----
------ d2 obj begin -----
object d2 vfptr addr is: 0x563b8f869ab8
object d2 vfptr[0] func ptr is: 0x563b8f8648d7
object d2 vfptr[0] func invoke res: Rhombus Run()
object d2 vfptr[1] func ptr is: 0x563b8f8645e4
object d2 vfptr[1] func invoke res: B RunB()
object d2 vfptr[2] func ptr is: 0x563b8f8647b0
object d2 vfptr[2] func invoke res: D2 RunD2()
object _b addr is: 0x7fff8b599938
object _b value is: 30
object _d2 addr is: 0x7fff8b59993c
object _d2 value is: 30
------ d2 obj end -----
object _rhombus addr is: 0x7fff8b599940
object _rhombus value is: 30
---------end rhombus common derive object inner memory layout test-------
|
3.内存布局示意图:
虚拟菱形继承类
简单实现代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| class D1_Virtual : virtual public B
{
public:
D1_Virtual(int var = 20) : B(var), _d1_virtual(var) {};
~D1_Virtual() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "D1_Virtual Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunD1_Virtual(void)
{
std::cout << "D1_Virtual RunD1_Virtual()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _d1_virtual;
};
class D2_Virtual : virtual public B
{
public:
D2_Virtual(int var = 20) : B(var), _d2_virtual(var) {};
~D2_Virtual() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "D2_Virtual Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunD2_Virtual(void)
{
std::cout << "D2_Virtual RunD2_Virtual()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _d2_virtual;
};
class Rhombus_Virtual : public D1_Virtual, public D2_Virtual
{
public:
Rhombus_Virtual(int var = 30) : D1_Virtual(var), D2_Virtual(var), _rhombus_virtual(var) {};
~Rhombus_Virtual() {}
public:
virtual void Run(void)
{
std::cout << "Rhombus_Virtual Run()" << std::endl;
}
virtual void RunRhombus_Virtual(void)
{
std::cout << "Rhombus_Virtual RunRhombus_Virtual()" << std::endl;
}
private:
int _rhombus_virtual;
};
|
Gcc命令的内存布局
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| Vtable for Rhombus_Virtual
Rhombus_Virtual::_ZTV15Rhombus_Virtual: 17 entries
0 32
8 (int
(...))(& _ZTI15Rhombus_Virtual)
24 (int
(...))D1_Virtual::RunD1_Virtual
40 (int
(...))-16
64 (int
(...))Rhombus_Virtual::_ZThn16_N15Rhombus_Virtual3RunEv
80 (int
(...))-32
112 (int
(...))Rhombus_Virtual::_ZTv0_n24_N15Rhombus_Virtual3RunEv
128 (int
(...))0
16 (int
(...))D1_Virtual::Run
32 (int
(...))-32
64 (int
(...))D1_Virtual::_ZTv0_n24_N10D1_Virtual3RunEv
80 (int
(...))0
16 (int
(...))D2_Virtual::Run
32 (int
(...))-16
64 (int
(...))D2_Virtual::_ZTv0_n24_N10D2_Virtual3RunEv
80 (int
|
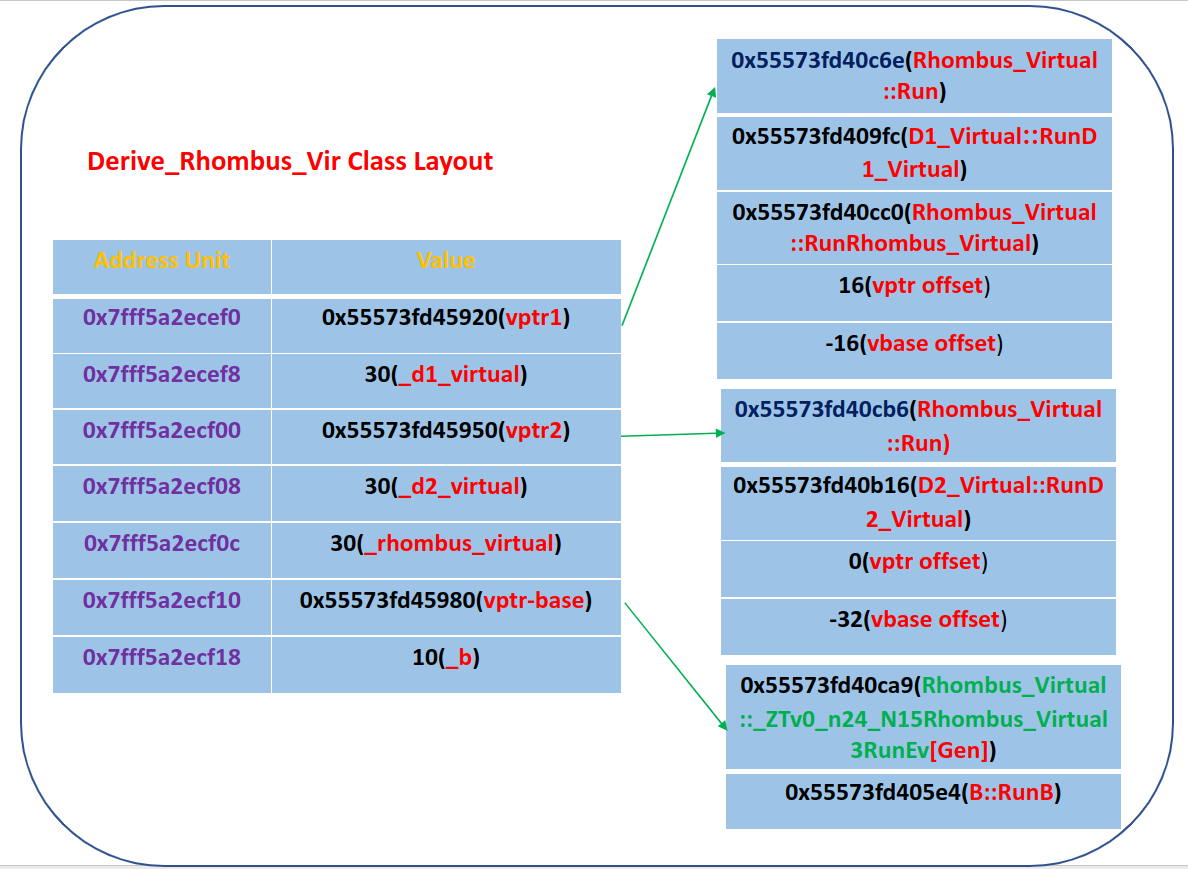
可以看到虚拟菱形继承类的内存空间特点是基类Di的内存布局(按照继承的顺序依次布局基类)+子类的成员变量+共同虚基类B的内存布局,基类Di的内存布局包括基类Di的虚函数表和虚基表和基类Di的成员变量。子类的虚函数在继承而来的第一个继承的Di基类的虚函数表基础上进行新增子类操作(新的虚函数)。可以看到虚拟菱形继承内存中只存在一份公共基类B的结构,这样可以解决二义性问题
内存布局的代码验证
1.测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| void RhombusVirtualDeriveTest(void)
{
Rhombus_Virtual d;
std::cout << "---------begin rhombus virtual derive object inner memory layout test-------" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object size is: " << sizeof(d) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object addr is: " << &d << std::endl;
std::cout << " typeid(d) is: " << typeid(d).name() << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d1 obj begin -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr addr is: " << (long*)&d << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr value is: " << (long*)*(long*)&d << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[0] func ptr is: " << (long*)*(long*)(*(long*)&d) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[0] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRun = (pFunc)(*(long*)(*(long*)&d));
(*pRun)();
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[1] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[1] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunD1 = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 1));
(*pRunD1)();
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[2] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vfptr[2] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunRhombus = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 2));
(*pRunRhombus)();
std::cout << " object d1 vptr offset is: " << (int)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 3) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d1 vbase offset is: " << (int)*((long*)(*(long*)&d) + 4) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d1_virtual addr is: " << (long*)&d + 1 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d1_virtual value is: " << (int)*((long*)&d + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d1 obj end -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d2 obj begin -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr addr is: " << (long*)&d + 2 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr value is: " << (long*)*((long*)&d + 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[0] func ptr is: " << (long*)*(long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[0] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRun2 = (pFunc)(*(long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)));
(*pRun2)();
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[1] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vfptr[1] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunD2 = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 1));
(*pRunD2)();
std::cout << " object d2 vptr offset is: " << (int)*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 2) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object d2 vbase offset is: " << (int)*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 2)) + 3) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d2_virtual addr is: " << (long*)&d + 3 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _d2_virtual value is: " << (int)*((long*)&d + 3) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _rhombus_virtual addr is: " << (long*)((int*)((long*)&d + 3) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _rhombus_virtual value is: " << *((int*)((long*)&d + 3) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ d2 obj end -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ base obj begin -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << " object base vfptr addr is: " << (long*)&d + 4 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object base vfptr value is: " << (long*)*((long*)&d + 4) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object base vfptr[0] func ptr is: " << (long*)*(long*)(*((long*)&d + 4)) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object base vfptr[1] func ptr is: " << (long*)*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 4)) + 1) << std::endl;
std::cout << " object base vfptr[1] func invoke res: ";
pFunc pRunB = (pFunc)(*((long*)(*((long*)&d + 4)) + 1));
(*pRunB)();
std::cout << " object _b addr is: " << (long*)&d + 5 << std::endl;
std::cout << " object _b value is: " << (int)*((long*)&d + 5) << std::endl;
std::cout << "------ base obj end -----" << std::endl;
std::cout << "---------end rhombus virtual derive object inner memory layout test-------" << std::endl;
}
|
2.运行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| ---------begin rhombus virtual derive object inner memory layout test-------
object size is: 48
object addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecef0
typeid(d) is: 15Rhombus_Virtual
------ d1 obj begin -----
object d1 vfptr addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecef0
object d1 vfptr value is: 0x55573fd45920
object d1 vfptr[0] func ptr is: 0x55573fd40c6e
object d1 vfptr[0] func invoke res: Rhombus_Virtual Run()
object d1 vfptr[1] func ptr is: 0x55573fd409fc
object d1 vfptr[1] func invoke res: D1_Virtual RunD1_Virtual()
object d1 vfptr[2] func ptr is: 0x55573fd40cc0
object d1 vfptr[2] func invoke res: Rhombus_Virtual RunRhombus_Virtual()
object d1 vptr offset is: 16
object d1 vbase offset is: -16
object _d1_virtual addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecef8
object _d1_virtual value is: 30
------ d1 obj end -----
------ d2 obj begin -----
object d2 vfptr addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecf00
object d2 vfptr value is: 0x55573fd45950
object d2 vfptr[0] func ptr is: 0x55573fd40cb6
object d2 vfptr[0] func invoke res: Rhombus_Virtual Run()
object d2 vfptr[1] func ptr is: 0x55573fd40b16
object d2 vfptr[1] func invoke res: D2_Virtual RunD2_Virtual()
object d2 vptr offset is: 0
object d2 vbase offset is: -32
object _d2_virtual addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecf08
object _d2_virtual value is: 30
object _rhombus_virtual addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecf0c
object _rhombus_virtual value is: 30
------ d2 obj end -----
------ base obj begin -----
object base vfptr addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecf10
object base vfptr value is: 0x55573fd45980
object base vfptr[0] func ptr is: 0x55573fd40ca9
object base vfptr[1] func ptr is: 0x55573fd405e4
object base vfptr[1] func invoke res: B RunB()
object _b addr is: 0x7fff5a2ecf18
object _b value is: 10
------ base obj end -----
---------end rhombus virtual derive object inner memory layout test-------
|
3.内存布局示意图:
总结
本篇主要介绍了C++类在菱形继承体系下类对象内存特点。可以看出,对于普通菱形继承继承,最终的子类对象中会存在共同基类的多份拷贝,当子类调用共同基类中的相同函数时会存在二义性问题,为了解决这个问题,最好是在第二层继承体系中使用虚拟继承,这样在最终的子类的内存中会仅有一个共同基类的拷贝,主要是因为最终子类的多个虚基表都指向同一个虚基类,对于虚函数表依然遵守前几篇介绍的基本原则,由于菱形继承肯定是多重继承,所以最终子类有多张虚函数表,对于虚拟情况下的菱形继承还存在多张虚基表

